Why energy storage?
With increasing global demand for renewably generated power and other clean technologies, the widespread adoption of energy storage continues to be described as the key game changer for electricity systems.
Reliable storage systems are a critical missing link between intermittent renewable power and a reliable net-zero carbon future. Beyond solving this main challenge, energy storage is being increasingly considered to meet other needs such as relieving grid congestion or smoothing out the variations in power that occur independent of renewable-energy generation. It makes sense with increasing power demands, increasing investments into solar and wind that we want to facilitate storing that energy using innovative battery technologies.
Battery storage is a future-proof industry if we use similar trends and increasing demand we’ve seen in the solar industry; the storage sector is learning and growing in the right direction. Non-subsidies business models are becoming more profitable with a decreased ROI time. Battery technologies are innovating so quickly and Nilar is really at the forefront of the industry’s innovation.
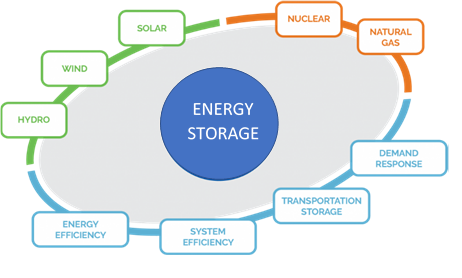
Energy storage really does sit in the middle of this circle.
Saves Money
Energy storage can save operational costs in powering the grid, as well as save money for electricity consumers who install energy storage in their homes and businesses. Energy storage can reduce the cost to provide services such as frequency regulation as well as offset the costs to consumers by storing low-cost energy and using it later, during peak periods at higher electricity rates.
By using energy storage during brief outages, businesses can avoid costly disruptions and continue normal operations. Residents can save themselves from lost food and medicines, and the inconvenience of not having electricity. Also, there will be options for both businesses and residential consumers to participate in demand response programs when available.
Improve Reliability & Resilience
Energy storage can provide backup power during disruptions. The same concept that applies to backup power for an individual device (e.g. a smoke alarm that plugs into a home but also has battery backup) can be scaled up to an entire building or even a micro-grid at large.
Storage provides flexibility for the grid, to ensure uninterrupted power to consumers, whenever and wherever they need it. This flexibility is critical to both reliability and resilience. As the cost of outages continues to rise, the value of enhanced reliability and improvements in resilience also increases.
Integrate Diverse Resources
Energy storage can smooth out the delivery of variable or intermittent resources such as wind and solar, by storing excess energy when the wind is blowing and the sun is shining and delivering it when there is a lack of renewable power input. But storage can also support the efficient delivery of electricity for inflexible, baseload resources. When demand changes quickly and flexibility is required, energy storage can inject or extract electricity as needed to exactly match the load – wherever, and whenever it’s needed. Energy storage is the enabling technology.
Reduce Environmental Impacts
In simplest terms, energy storage enables electricity to be saved for later, when and where it is most needed. This creates efficiencies and capabilities for the electric grid—including the ability to reduce greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions.
By introducing more flexibility into the grid, energy storage can help integrate more solar, wind and distributed energy resources. It can also improve the efficiency of the grid – increasing the capacity factor of existing resources – and offset the need for building new pollution-emitting peak power plants.
As our energy supply mix gets cleaner with low- and no-carbon resources, energy storage helps that supply mix to evolve more easily and reliably.